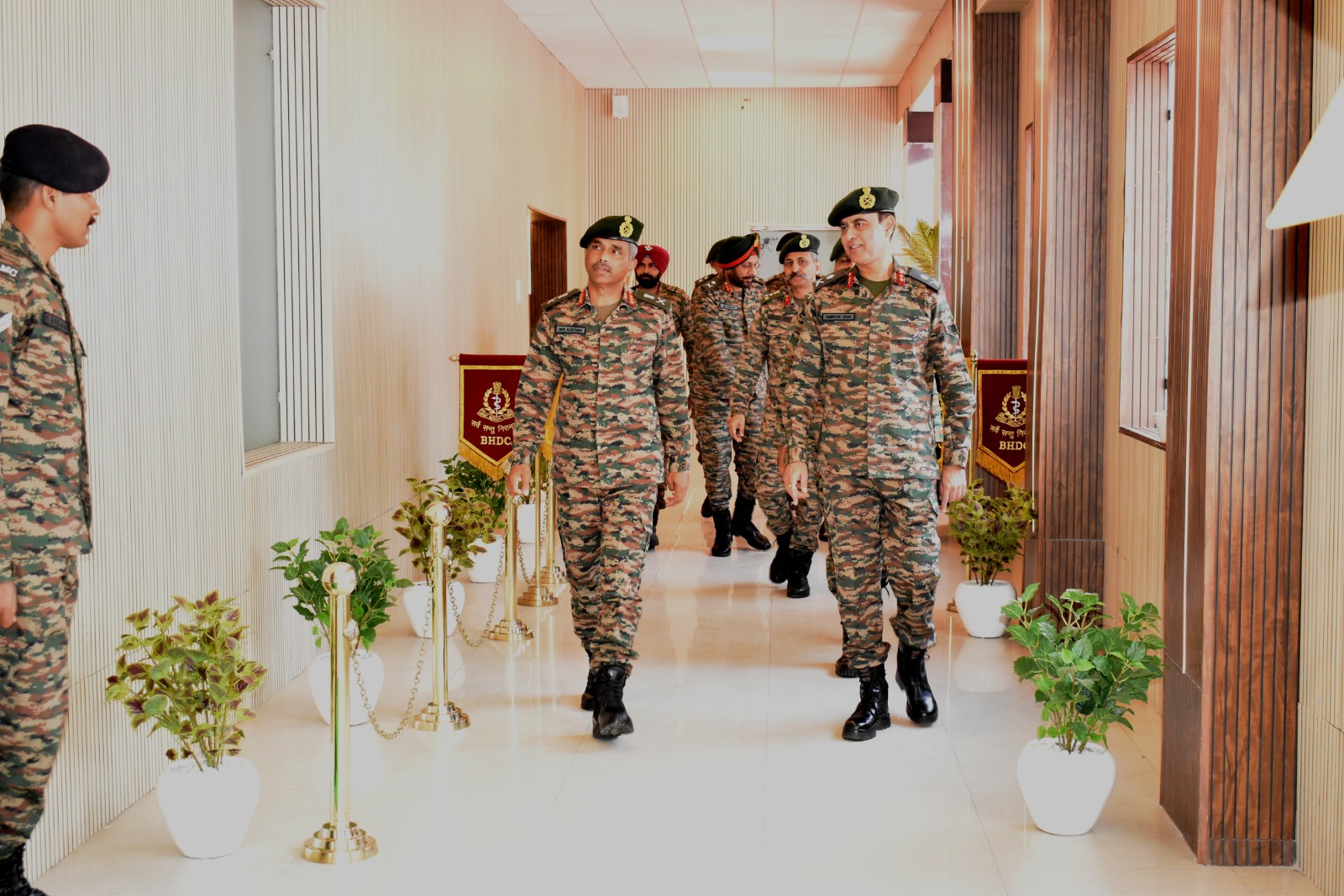
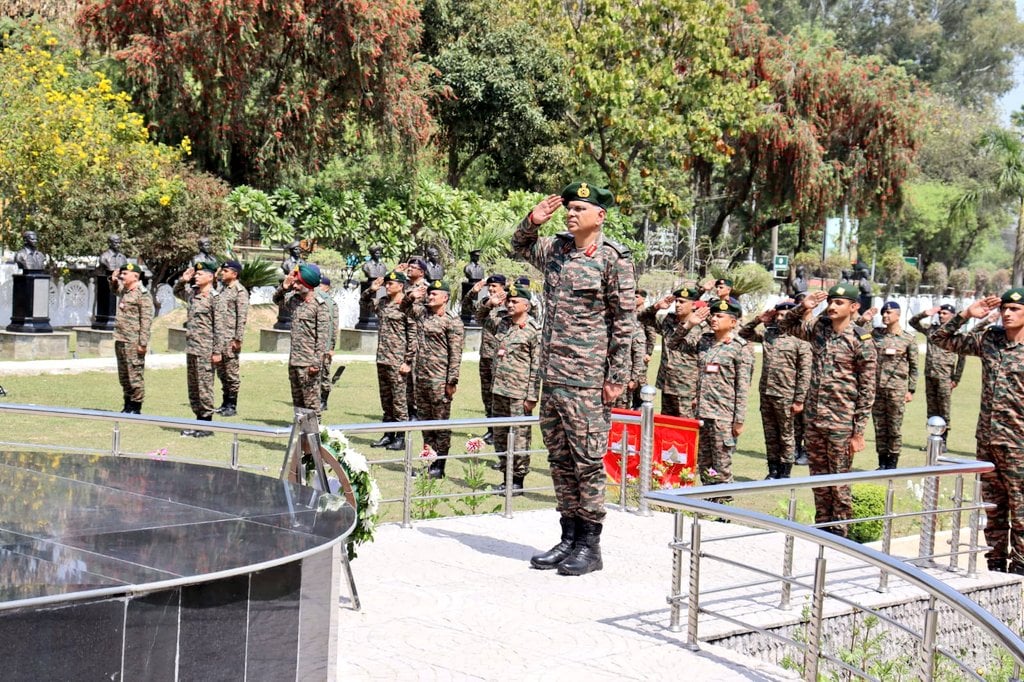
Lt Gen Manoj Kumar Katiyar Inspects Base Hospital Delhi Cantt, Emphasizes Quality Healthcare for Armed Forces
Delhi, April 1, 2025 – Lieutenant General Manoj Kumar Katiyar, PVSM, AVSM, General Officer Commanding-in-Chief of the Western Command, conducted…
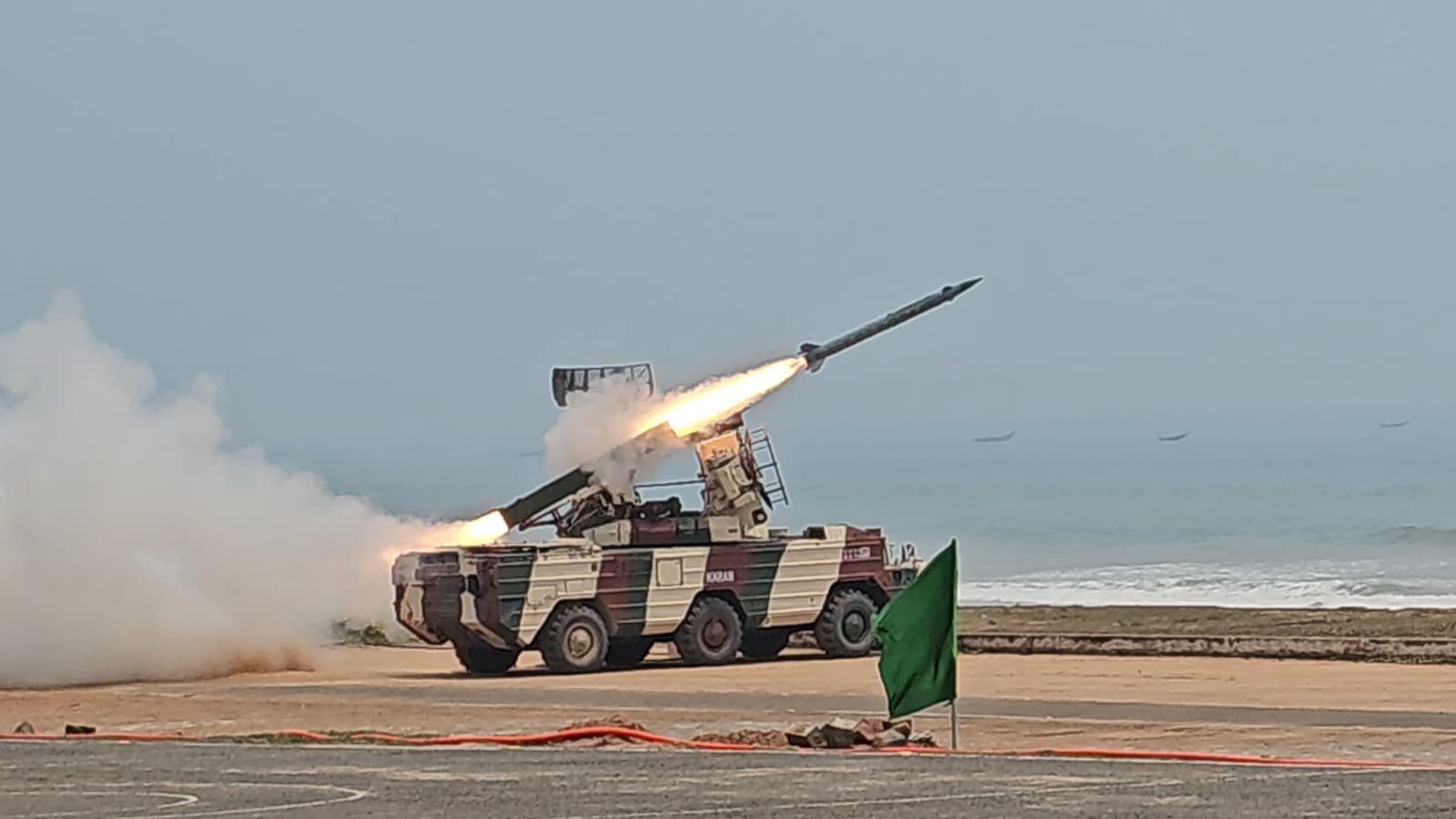
Indian Army’s White Tiger Division Demonstrates Air Defense Prowess with Successful OSA-AK Missile Firing at Gopalpur
The Indian Army’s White Tiger Division, under the Southern Command, showcased its operational readiness and technical expertise in a live…
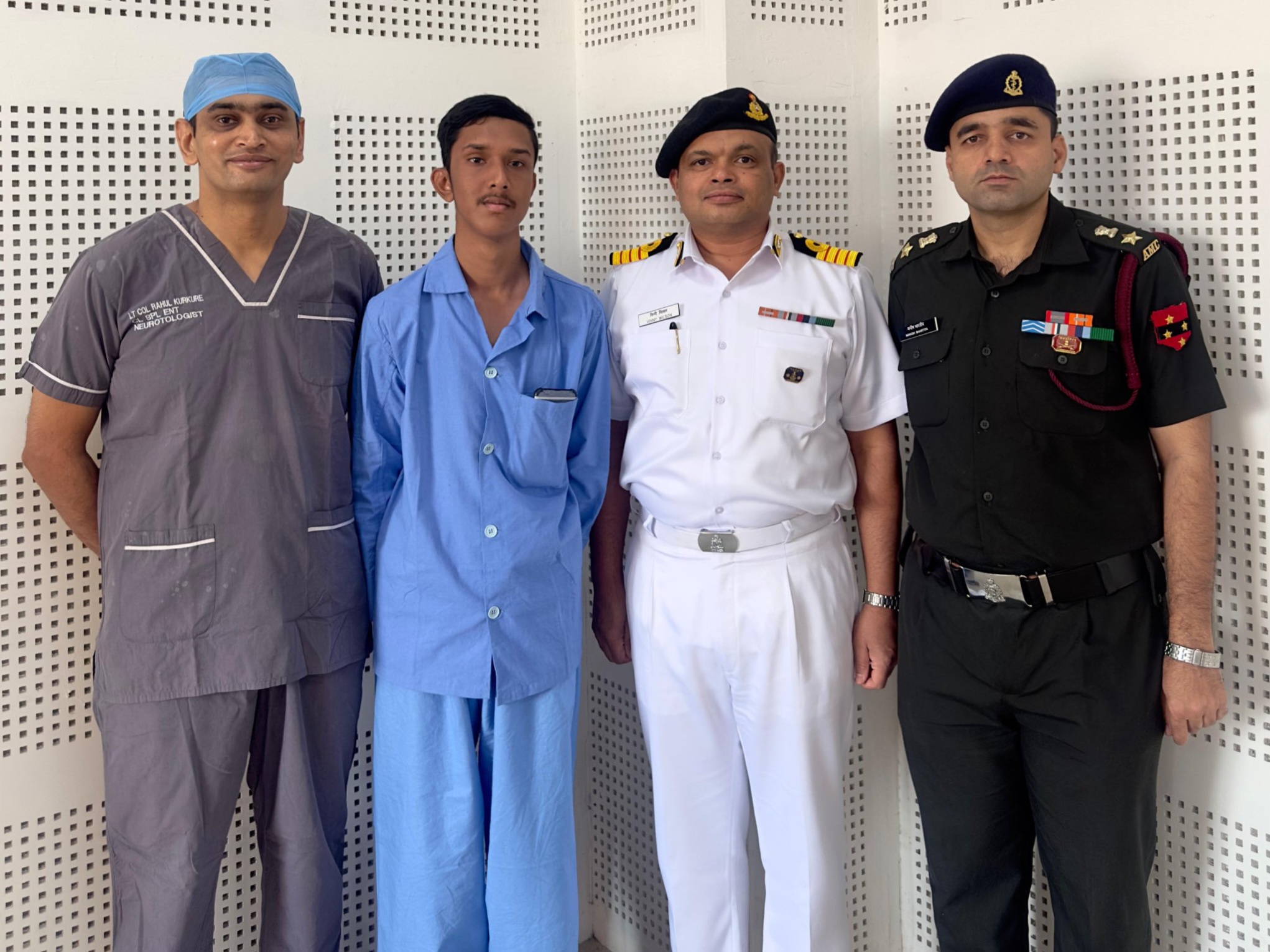
Indian Army’s Command Hospital in Pune Achieves Medical Breakthrough, Treats Rare Inner Ear Disorder in Bangladeshi Teen
Pune, April 1, 2025 – In a remarkable display of medical excellence and international collaboration, the Command Hospital of the…
Mahindra to Supply 1,986 Scorpio Pik-Ups to Indian Army Under ₹2,700 Crore Deal
In a significant development bolstering the indigenous defence ecosystem, Mahindra & Mahindra has signed a ₹2,700 crore contract with the…
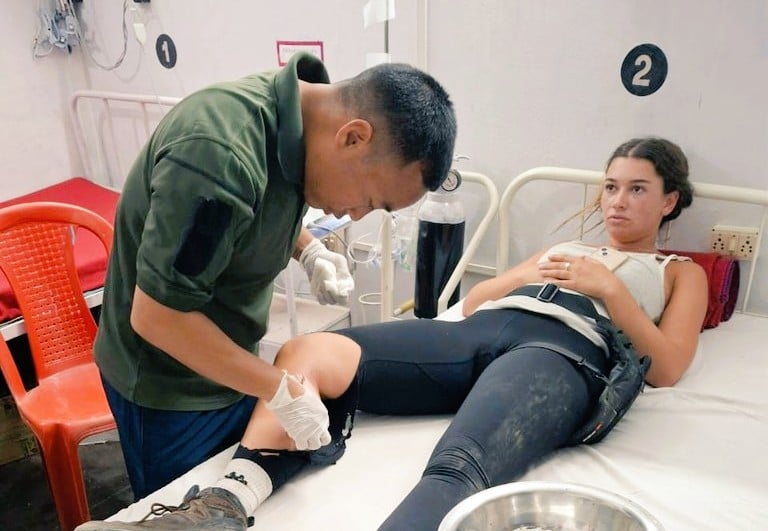
BSF Soldier Provides Timely Medical Aid to Israeli Female tourist
In a remarkable display of humanity and swift action, the 04 Battalion of the Border Security Force (BSF), Meghalaya, came…
Lt Gen PK Mishra Takes Over Command of White Knight Corps
Lt Gen PK Mishra, AVSM, YSM, SM, assumed command of the prestigious White Knight Corps from Lt Gen Navin Sachdeva,…