“Operation Safed Sagar was a turning point for the Indian Air Force, proving that air power, when used decisively, can change the course of war. The lessons learned continue to shape our doctrine and modernization.” – Former Air Marshal B.S. Dhanoa
On 26 May 1999, the Indian Air Force (IAF) launched Operation Safed Sagar, this was the first large-scale use of air power in the Kashmir region since the 1971 Indo-Pak War. Never before had an air force been tasked with such high-altitude precision operations in rugged mountainous terrain—making it a watershed moment in military aviation history.
This pivotal mission not only changed the war’s outcome but also transformed India’s air power doctrine. Over the last 26 years, the IAF has modernized dramatically to face new challenges like drone warfare, precision strikes, and hybrid threats, making it a future-ready force for India’s defense.
A Turning Point in Indian Military History
Operation Safed Sagar, launched in 1999, was a pivotal air campaign initiated in response to the infiltration and occupation of strategic peaks by Pakistani forces in the Kargil sector along the Line of Control (LoC). This operation marked the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) first major combat air operation since the 1971 war and tested its ability to conduct high-altitude warfare under extremely challenging conditions. The terrain in Kargil, with altitudes exceeding 15,000 feet, presented some of the most difficult flying and bombing environments in the world—thin air, rugged mountains, and unpredictable weather made precision targeting and sustained aerial operations extraordinarily complex.
To support the Indian Army’s efforts in evicting entrenched intruders, the IAF deployed key assets such as the Mirage-2000 and MiG series fighter jets for precision bombing and ground-attack missions. These aircraft, equipped with laser-guided bombs, were able to neutralize fortified enemy positions while minimizing collateral damage. Additionally, Mi-17 helicopters played a vital role in troop transportation, casualty evacuation, and logistical support in the inaccessible mountainous terrain. The IAF operated under strict constraints, including a prohibition on crossing the LoC, which required innovative tactics and exceptional coordination with ground forces to achieve maximum impact without escalating the conflict.
Despite the operational difficulties and risks, the IAF demonstrated remarkable precision, adaptability, and bravery. The sacrifices of pilots like Squadron Leader Ajay Ahuja and Flight Lieutenant Kambampati Nachiketa stand as poignant reminders of the human cost of the conflict. Squadron Leader Ahuja’s MiG-21 was shot down during a reconnaissance mission, and Flight Lieutenant Nachiketa was lost while executing bombing runs; their valor exemplified the courage and commitment of the IAF personnel involved in the campaign. These losses, while tragic, galvanized the force and underscored the gravity of the mission.


Operation Safed Sagar proved critical in regaining control over the strategically vital heights in the Kargil sector, which were crucial for ensuring the security of key supply routes and maintaining the territorial integrity of India. The air campaign, in close coordination with ground operations, played a decisive role in turning the tide of the conflict in India’s favor. It highlighted the importance of air power in mountainous warfare and led to significant lessons that shaped future modernization and doctrinal reforms within the IAF. The success of Safed Sagar remains a defining chapter in India’s military history, symbolizing resilience, tactical innovation, and the indomitable spirit of the Indian Air Force.
Post-Kargil Reforms: Modernizing the Indian Air Force
The Kargil conflict exposed critical gaps in India’s air capabilities, intelligence, and joint operations. In response, the Indian Air Force (IAF) undertook comprehensive reforms to bolster its operational readiness and strategic edge.
One major focus was fleet modernization. The induction of the powerful Su-30MKI fighter jets significantly enhanced air combat capabilities, while upgrades to the Mirage-2000 fleet improved precision strike potential and survivability in high-altitude conflict zones.

Infrastructure upgrades were another priority. The IAF modernized Advance Landing Grounds (ALGs) in strategic regions such as Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh, enabling rapid deployment and sustained operations in the challenging Himalayan terrain.

To overcome coordination challenges revealed during Kargil, the armed forces pushed for greater jointness and integration. This led to improved cooperation among the Army, Navy, and Air Force, eventually culminating in the creation of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) position to streamline unified command and operational planning.

Finally, surveillance and air defense capabilities were strengthened through enhanced radar networks and the integration of space-based monitoring systems. These advancements significantly improved early warning and situational awareness, crucial for timely and effective responses to emerging threats.
From Balakot to Eastern Ladakh: The IAF’s New Era of Air Superiority
The 2019 Balakot air strikes marked a bold and historic doctrinal leap for India’s defense strategy, signaling a significant shift in the country’s approach to cross-border threats. By conducting precision strikes deep across the Line of Control (LoC) into Pakistan-administered territory, the Indian Air Force (IAF) demonstrated not only its operational capability but also its willingness to adopt a more proactive and assertive posture in countering terrorism and hostile actions. This operation was unprecedented in its scale and precision, showcasing the IAF’s enhanced ability to carry out surgical strikes with minimal collateral damage while sending a clear message of deterrence to adversaries. The Balakot strikes underscored the growing confidence and modernization of the IAF, marking a milestone in India’s strategic doctrine by expanding the scope and reach of its air power beyond traditional defensive roles.
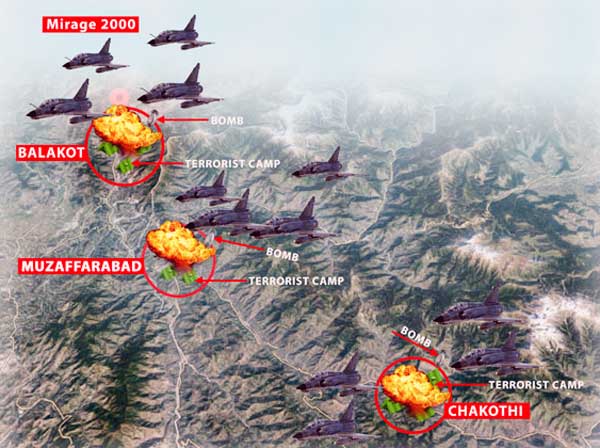
Following this, the IAF’s performance during the prolonged 2020–2023 standoff with China in Eastern Ladakh further highlighted the evolving role of air power in India’s military strategy. The rapid deployment and effective use of advanced aerial platforms such as Chinook heavy-lift helicopters, Apache attack helicopters, and the formidable Su-30MKI fighter jets played a crucial role in bolstering India’s defensive and offensive capabilities in the high-altitude and challenging terrain of Ladakh. These platforms enhanced troop mobility, reconnaissance, and close air support, ensuring that the Indian military maintained a credible deterrent posture during the tense border standoff. The integration of these sophisticated aircraft demonstrated the IAF’s improved operational readiness, enabling swift responses to emerging threats and maintaining sustained pressure on adversaries.
IAF’s performance in Operation Sindoor showcased enhanced capabilities in high-altitude combat, rapid deployment, and the use of advanced drones and precision-guided munitions. Their coordinated efforts with the Army ensured effective neutralization of hostile positions while minimizing collateral damage, demonstrating the IAF’s evolution since Kargil in terms of technology, strategy, and joint operations.
Also Read: India Becomes The First Country to Strike 11 Air Bases of a Nuclear Powered Country
Collectively, these operations emphasize the growing importance of air power as a central pillar of India’s defense strategy. There has been a noticeable increase in aerial patrols along critical borders, ensuring continuous surveillance and rapid reaction capability. Additionally, the IAF has intensified joint exercises with the Indian Army and Navy, enhancing interoperability and fostering a more integrated approach to national security. These developments reflect a broader strategic shift towards leveraging air dominance to secure India’s frontiers, project power, and maintain stability in a complex and evolving security environment. The experience gained from Balakot and the Ladakh standoff continues to shape the IAF’s modernization priorities, operational doctrines, and preparedness for future conflicts.
Rise of Drone Warfare and India’s Indigenous Defense Push
Modern warfare is rapidly evolving, with an increasing reliance on unmanned systems that offer greater precision, endurance, and risk mitigation compared to traditional manned platforms. Recognizing this shift, the Indian Air Force (IAF) has progressively incorporated a range of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) into its operational framework. Currently, the IAF deploys Heron drones for surveillance and reconnaissance missions, which provide critical real-time intelligence across sensitive borders. Additionally, India is in the process of acquiring the advanced MQ-9B Predator drones from the United States, a move that will significantly enhance its long-range strike and intelligence-gathering capabilities.

Alongside these acquisitions, the IAF is also heavily investing in the development of indigenous UAV technology, which aligns with the government’s Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative aimed at fostering self-reliance in defense manufacturing. Indigenous projects like the Defence Research and Development Organisation’s (DRDO) Rustom drone series, the Archer-NG by Bharat Elections Limited, and the Combat Air Teaming System (CATS) Warrior by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited are examples of India’s efforts to build a robust and versatile unmanned platform ecosystem. These homegrown systems are designed to complement manned aircraft, offering capabilities such as persistent surveillance, electronic warfare, and precision strikes, while reducing dependence on foreign technology.

In Operation Sindoor, drones played a pivotal role in enhancing battlefield intelligence, surveillance, and precision strike capabilities. The Indian Air Force deployed a mix of reconnaissance and armed drones to conduct real-time monitoring of enemy movements, identify strategic targets, and carry out precision attacks with minimal risk to personnel. These unmanned systems provided crucial situational awareness and helped neutralize hostile positions effectively, marking a significant shift toward drone-dominated modern warfare and highlighting the IAF’s growing reliance on indigenous and imported drone technology for future conflicts.

The strategic importance of unmanned systems was underscored by the 2021 drone attack on the Jammu Air Force Station, which served as a wake-up call for the Indian defense establishment. This incident accelerated investments in counter-drone technologies, emphasizing the urgent need for AI-enabled defense systems capable of detecting, tracking, and neutralizing hostile drones. These advancements are not only crucial for safeguarding critical military infrastructure but also represent a broader shift towards integrating artificial intelligence and automation into India’s defense architecture. By prioritizing indigenous development and cutting-edge countermeasures, the IAF is positioning itself to meet emerging threats effectively while reinforcing the country’s broader goal of defense self-sufficiency.
The Indian Air Force in 2025: Combat-Ready and Future-Focused
Today’s Indian Air Force (IAF) combines a diverse and advanced fleet of aircraft, including the state-of-the-art Rafale fighter jets, the indigenous Tejas Mk1A, and upgraded versions of the Su-30MKI. This modern mix of platforms significantly enhances the IAF’s combat capabilities across a wide range of missions, from air superiority and precision strikes to reconnaissance and close air support.
In addition to cutting-edge aircraft, the IAF has integrated advanced technologies to strengthen its operational edge. AI-powered command and control systems have improved decision-making speed and accuracy, allowing commanders to process complex battlefield information more effectively. Electronic warfare suites provide the IAF with enhanced capabilities to disrupt enemy communications and radar systems, thereby gaining a tactical advantage during engagements. Space-based surveillance assets further augment situational awareness by enabling real-time monitoring of strategic areas, making early warning and threat detection more efficient.
Also Read: What is Integrated Air Command & Control System (IACCS) ?
Regular participation in multinational exercises with allied air forces has also played a crucial role in elevating the IAF’s operational capability. These joint exercises foster interoperability, improve tactical coordination, and expose Indian pilots and commanders to diverse combat doctrines and technologies. This collaborative approach not only strengthens bilateral and multilateral defense ties but also ensures that the IAF remains agile and prepared to face complex security challenges alongside its global partners.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Indian Air Power
By 2030, the Indian Air Force (IAF) envisions a transformative leap in its capabilities, driven by cutting-edge technologies and strategic reforms aimed at addressing evolving security challenges in the region. One of the most significant advancements planned is the integration of hypersonic weapons—missiles capable of traveling at speeds greater than five times the speed of sound. These weapons will provide India with a decisive edge by enabling rapid, long-range precision strikes that are extremely difficult to detect or intercept, thereby enhancing deterrence against potential adversaries.
Alongside hypersonic weapons, the IAF is aggressively pursuing the development and deployment of stealth drones. These unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), designed with low radar visibility and advanced autonomous capabilities, will revolutionize intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance (ISR), and strike missions. Stealth drones will be able to penetrate deep into enemy airspace with minimal risk of detection, gathering critical real-time intelligence or executing precision attacks while reducing the exposure of human pilots to danger. This shift towards unmanned and semi-autonomous platforms reflects the IAF’s commitment to leveraging emerging technologies to maintain air superiority in increasingly complex and contested environments.
In parallel, the expansion of India’s space warfare capabilities is another pillar of the IAF’s future strategy. Space is rapidly becoming a contested domain, with adversaries investing heavily in anti-satellite weapons, space-based sensors, and cyber capabilities targeting space infrastructure. Recognizing this, the IAF is working to develop resilient space-based surveillance, communication, and navigation systems that will ensure uninterrupted command and control of military assets. Enhanced space capabilities will also enable early warning systems and bolster India’s ability to monitor threats across its vast borders, adding a vital layer to its multi-domain defense posture.
A crucial organizational reform supporting these technological advances is the ongoing establishment of joint theatre commands. These commands are designed to integrate the Army, Navy, and Air Force under unified leadership for specific geographic or operational theatres. Such integration will allow for seamless coordination and faster decision-making across the services, thereby maximizing the effectiveness of India’s military response to multi-dimensional threats. This jointness is particularly important given the complex security environment posed by China’s growing military assertiveness along the northern borders and Pakistan’s persistent cross-border challenges. By operating under a unified command structure, the armed forces will be better positioned to execute coordinated operations that leverage the unique strengths of each service.
Looking ahead, air power will continue to be a cornerstone of India’s national security strategy, but its role will evolve far beyond traditional air superiority and ground support missions. The IAF is preparing to operate effectively across land, air, and space domains, creating a truly integrated defense network capable of addressing threats that are increasingly hybrid, multi-domain, and technology-driven. This comprehensive approach, combining advanced weapons systems, unmanned technologies, space capabilities, and joint operational doctrines, will ensure that India maintains a robust deterrence posture and a decisive edge in safeguarding its sovereignty and strategic interests well into the coming decades.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Operation Safed Sagar
Operation Safed Sagar was far more than a mere battle; it represented a pivotal moment and a powerful catalyst that fundamentally reshaped India’s air warfare doctrine. The challenges faced during the Kargil conflict exposed critical gaps in high-altitude combat, precision targeting, and joint operations, compelling the Indian Air Force (IAF) to undergo rapid transformation and modernization. This operation became a defining chapter that not only tested the valor and skill of the IAF’s pilots and personnel but also set the stage for a broader strategic evolution in how air power would be envisioned and employed in India’s defense framework.
From those early days of relying heavily on manned fighter jets such as the Mirage-2000 and MiG fighters operating under severe constraints, the IAF’s journey has been marked by resilience, adaptability, and a relentless pursuit of technological innovation. The lessons learned from Safed Sagar spurred investments in advanced aircraft, improved surveillance and reconnaissance systems, and the integration of cutting-edge weapons technology. Over the years, this evolutionary process has propelled the IAF into the era of AI-driven drone dominance by 2025, where unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with sophisticated autonomous capabilities now play a central role in intelligence gathering, precision strikes, and electronic warfare.
This legacy of innovation and transformation continues to guide the IAF as it confronts an increasingly complex security environment characterized by rapid technological advancements and multifaceted threats. The force’s commitment to securing India’s skies has only grown stronger, driven by a vision that combines traditional aerial combat strengths with emerging domains such as space warfare, cyber operations, and artificial intelligence. The spirit of Operation Safed Sagar—defined by courage, sacrifice, and strategic foresight—remains embedded in the ethos of the IAF, inspiring every pilot, engineer, and strategist to push the boundaries of what is possible in defense of the nation.
In essence, Operation Safed Sagar laid the foundation for a modern, agile, and future-ready air force that embraces innovation while honoring its rich heritage. This journey from the rugged mountains of Kargil to the sophisticated battlefields of the 21st century exemplifies the IAF’s unwavering dedication to adapting and evolving in order to protect India’s sovereignty and maintain peace and stability in a rapidly changing world. The operation’s enduring impact is a testament to the IAF’s ability to learn from history, harness new technologies, and remain a formidable guardian of the nation’s skies for generations to come.













