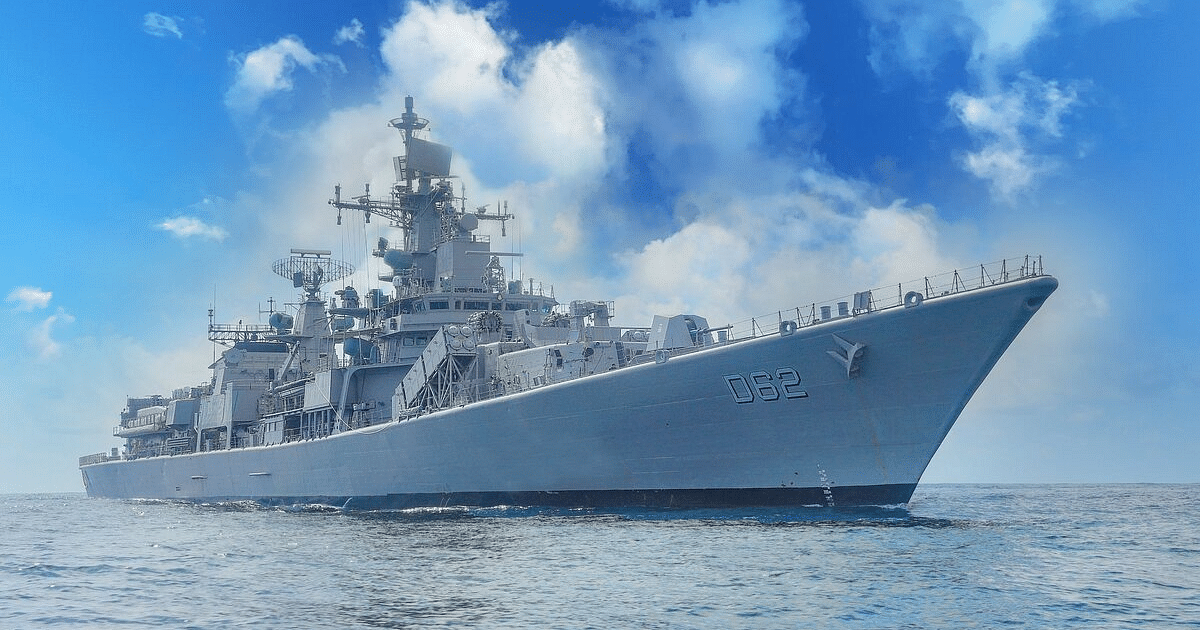
Germany’s TKMS Sees India as Potential Global Hub for Submarine and Warship Production
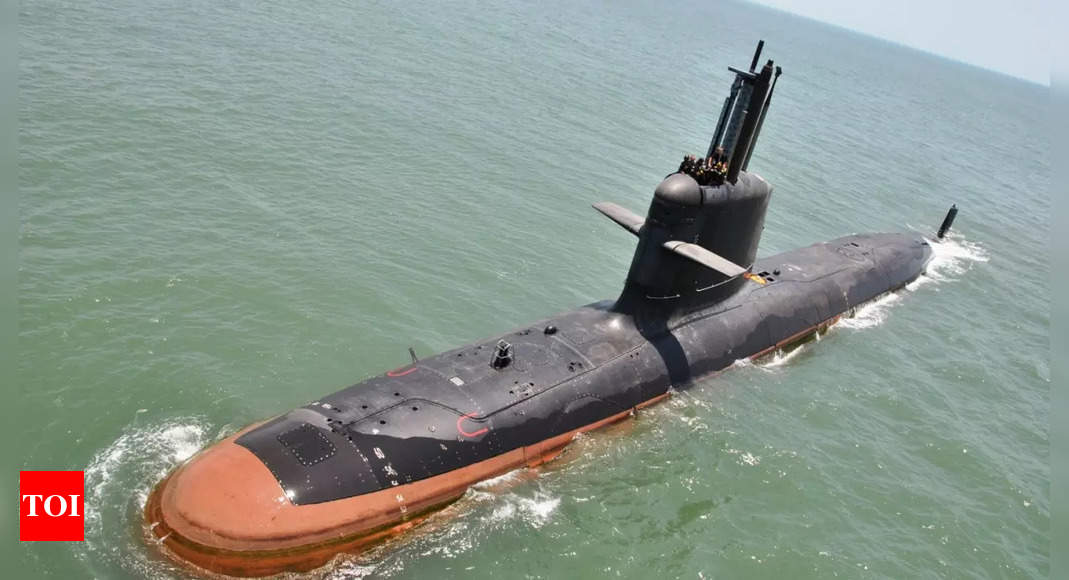
In a significant move to tap into India’s potential as a center for maritime defense production, Thyssenkrupp Marine Systems (TKMS),…
TKMS Aims to Build Submarines for Indian Navy, Proposes Warship Construction Hub
Thyssenkrupp Marine Systems (TKMS), a leading maritime firm in Germany, is actively vying for a significant contract to construct six…
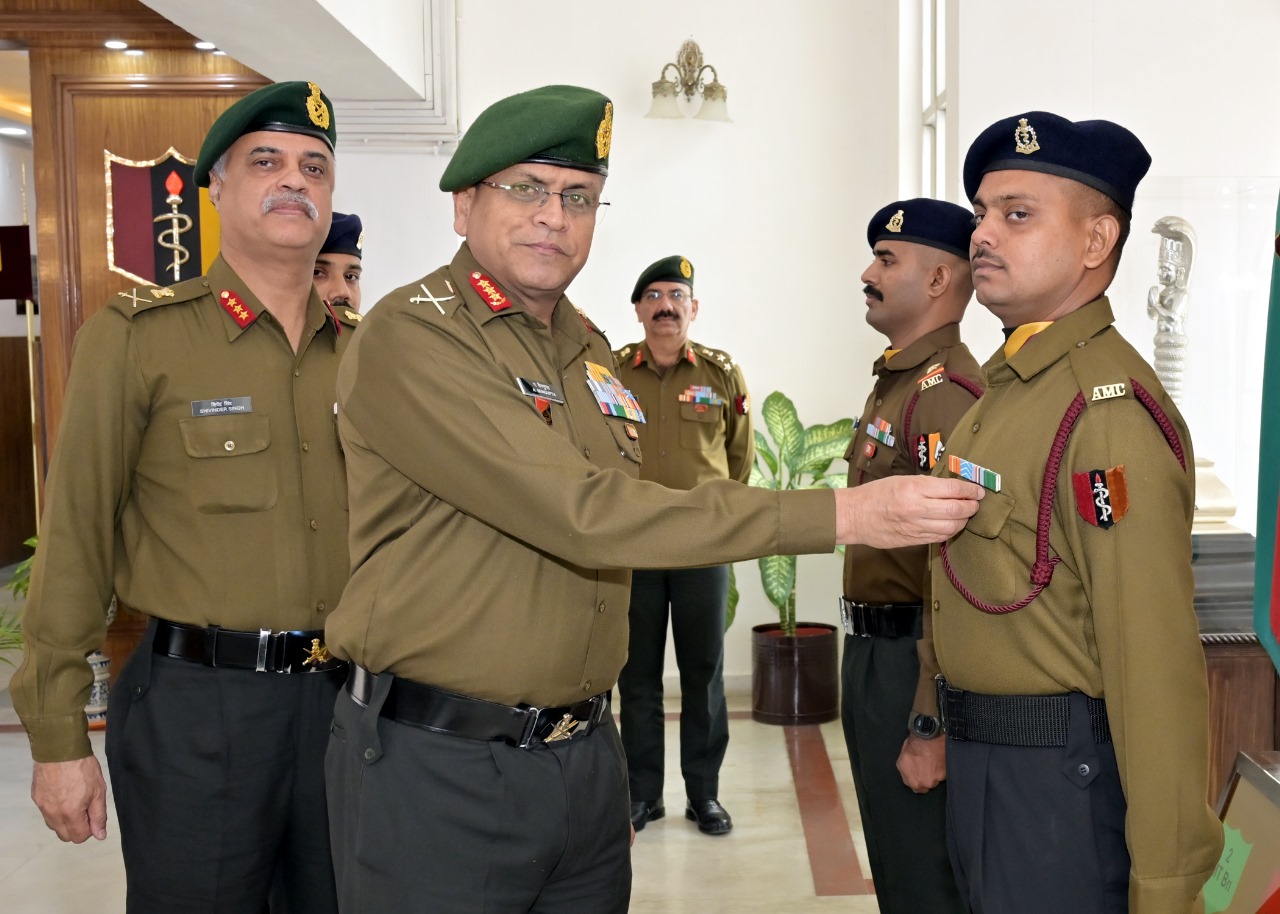
Lt General Anindya Sengupta Reviews Preparedness at AMC Centre and College Lucknow
Lt Gen Anindya Sengupta, General Officer Commanding-in-Chief (GOC-in-C) of Central Command, visited the Army Medical Corps (AMC) Centre and College,…
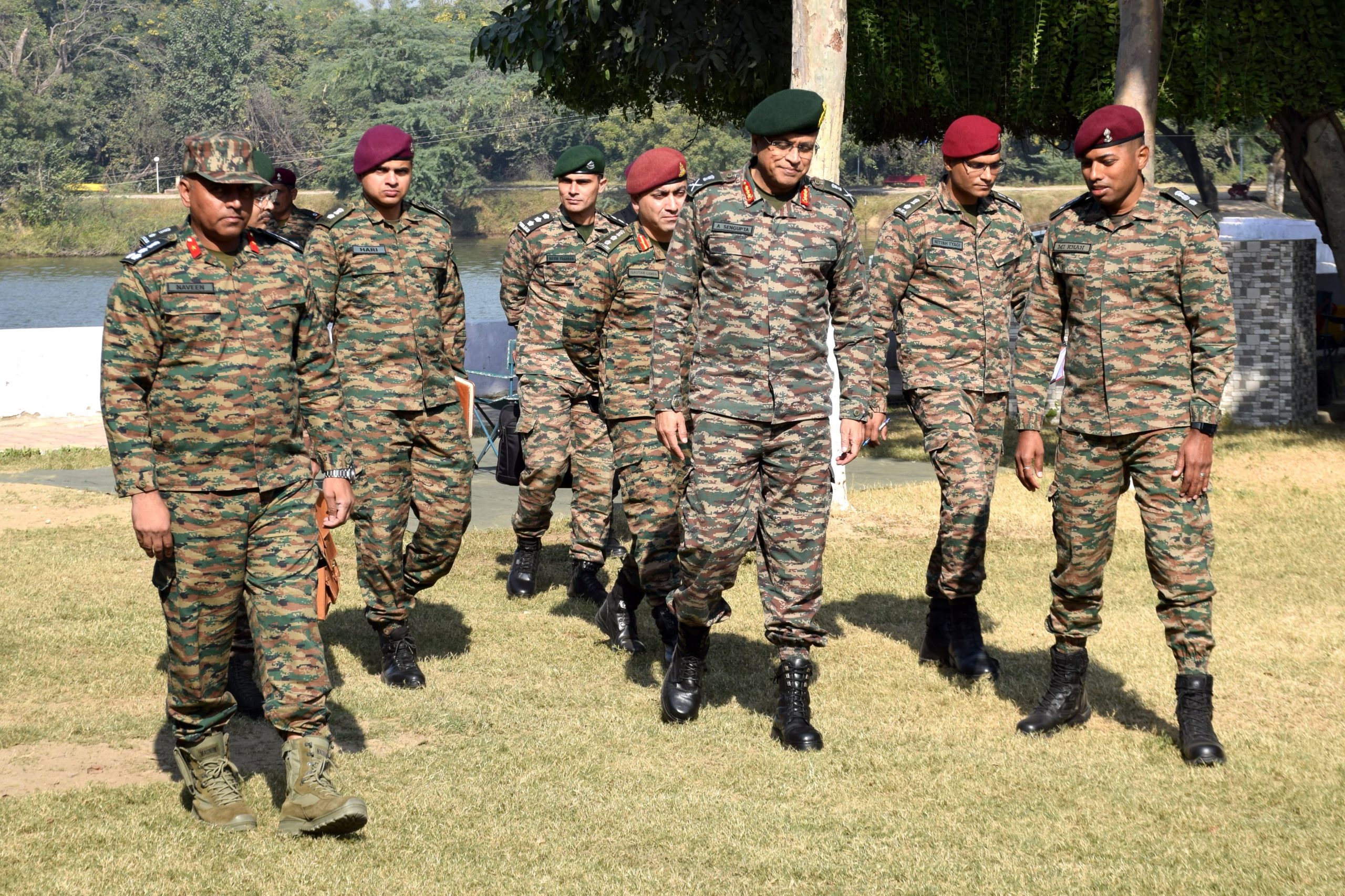
Lt General Anindya Sengupta Reviews Operational Readiness of Shatrujeet Brigade
Lt Gen Anindya Sengupta, General Officer Commanding-in-Chief (GOC-in-C) of Central Command, visited the Shatrujeet Brigade to assess its operational readiness…
Indian Army’s Eastern Command to Host “TATA Steel Kolkata 25 Km – Vijay Diwas Cup” on December 15 to Honor 1971 War Heroes
The Indian Army’s Eastern Command is set to host the "TATA Steel Kolkata 25 Km - Vijay Diwas Cup" on…
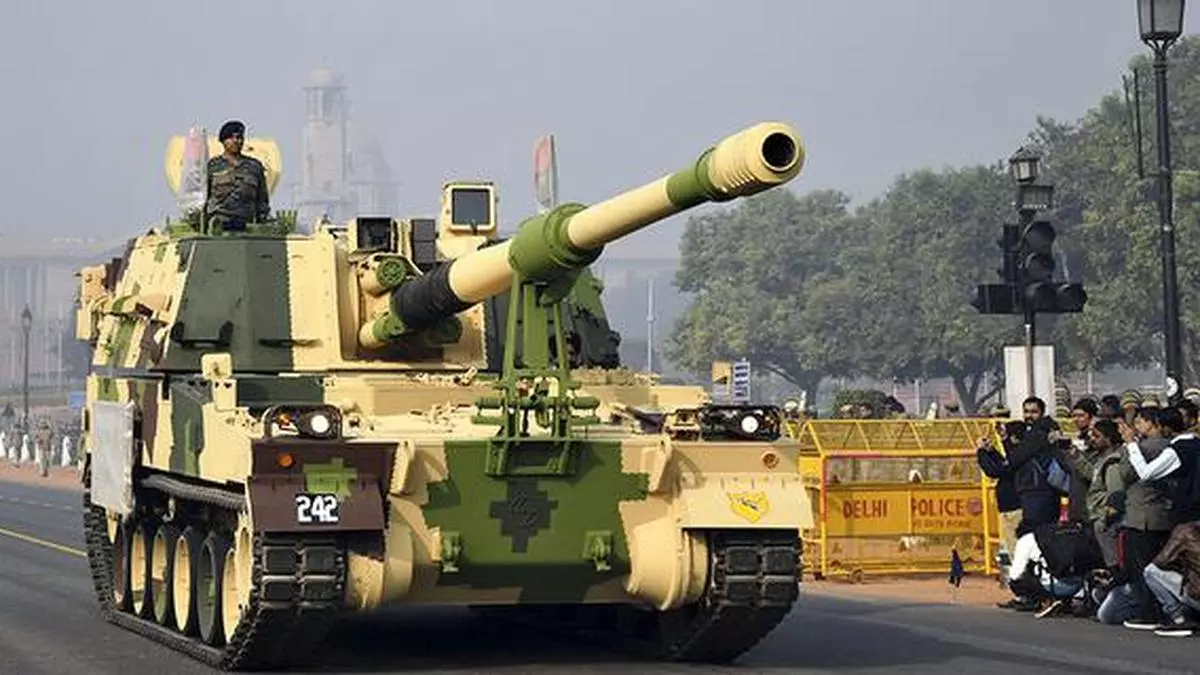
Indian Army Secures Approval for Procurement of 100 K-9 Self-Propelled Howitzers
The Indian Army is poised to significantly enhance its artillery capabilities following the endorsement of a proposal to procure 100…