Another Pakistani Fighter Jet Shot Down in Pathankot
In a dramatic escalation of cross-border tensions, a Pakistani Air Force jet was shot down by Indian air defence systems…
India Intercepts Pakistani Missiles and Loitering Munitions Targetting Key Areas in Jammu & Kashmir
India’s air defense forces successfully intercepted missiles and loitering munitions launched by Pakistan targeting key areas in Jammu and Kashmir,…
Pakistan’s Army Chief Asim Munir Reportedly Arrested by CJCSC
In a stunning development shaking Pakistan’s military and political landscape, Pakistan Army Chief General Asim Munir has reportedly been arrested…
Pakistan F-16 Shot Down by Indian Surface-to-Air Missile Near Sargodha Air Base
In a significant escalation along the India-Pakistan border, an F-16 fighter jet of the Pakistan Air Force was shot down…
Pakistan Loses Two JF-17 Fighter Jets Amid Escalating Tensions with India
In a decisive show of air superiority, the Indian Armed Forces on Wednesday shot down a Pakistani JF-17 fighter jet…
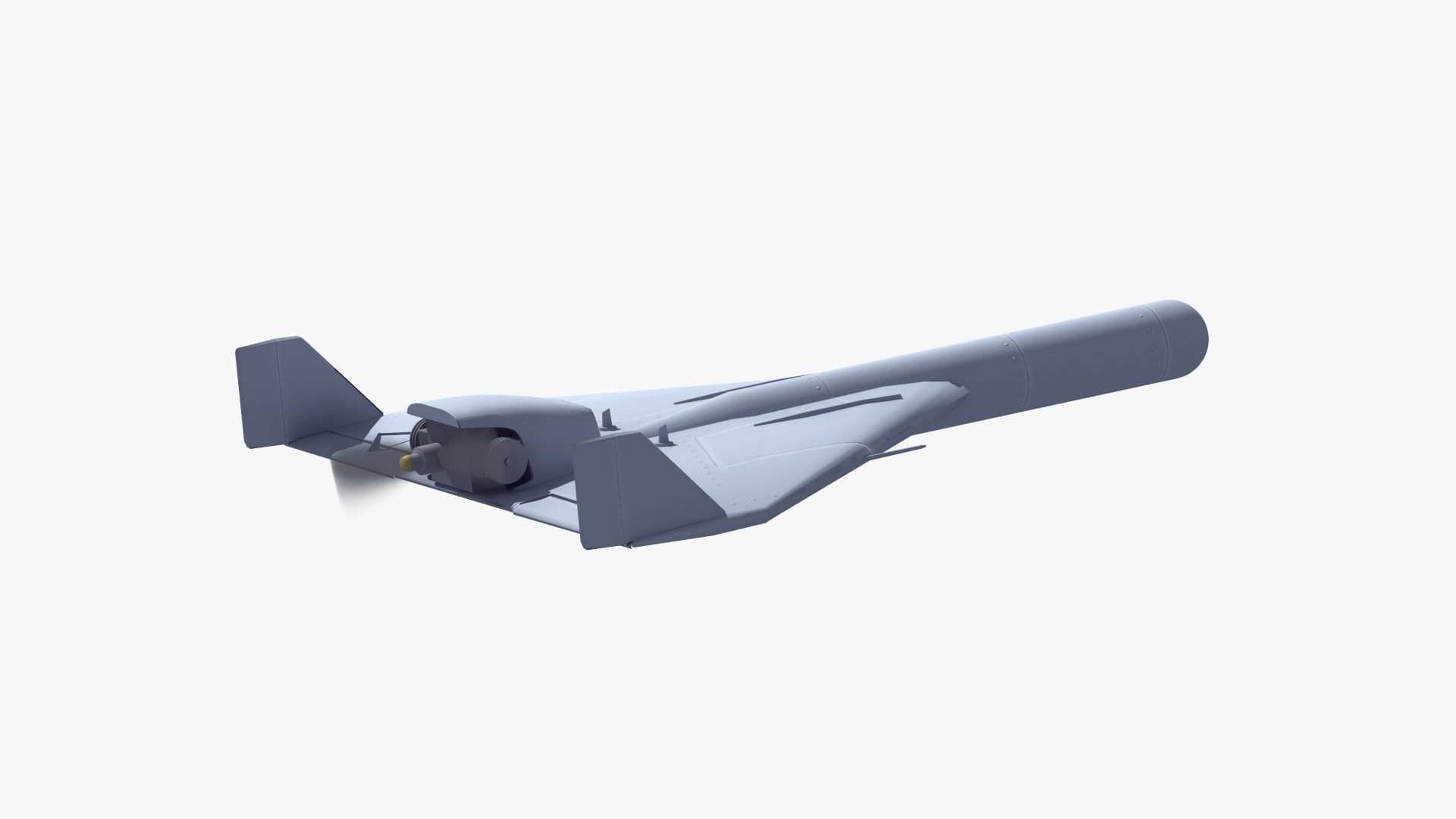
India Deploys Harpy Drones in Precision Strikes on Pakistani Air Defenses
In a significant escalation of hostilities along the Line of Control (LoC), the Indian Armed Forces have launched precision strikes…